- About
Getting to know us
- Services
- Managed Services
- Application Services
- Cloud Services
- Data Science
- Consulting Services
- Technology Solutions
Managed Services
Application Services
Data Science
Consulting Services
Technology Solutions
- Industries
- Resources
Resources
- Contact
- Contact us
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Network Components Overview
Contents
The aim of this blog is to introduce you to the key virtual networking components within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). We will explore the main resources within a Virtual Cloud Network and what they are used for.
Once your tenancy has been provisioned; you will need to create a Compartment. A compartment is a collection of related resources such as VM instances, virtual cloud networks, and block volumes that can be accessed only by certain groups that have been given permission by an administrator.
Under the newly created resource, you will need to create the Virtual Cloud Network (VCN). A virtual cloud network acts like a traditional network setup. Within the Virtual Cloud Network, multiple resources reside such as Subnets, Gateways, Route Rules and much more. You need to set up at least one VCN before you can run an instance.
I will briefly explain what each resource’s function is:
CIDR Blocks - Required
The VCN size range in OCI is limited from /16 to /30. A CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing or supernetting. The CIDR block method replaces the traditional subnet class of IP allocation (Class, A, B, C).
CIDR Blocks are two sets of numbers. First, the network (e.g. 10.1.0.0). Next, the suffix, this indicates how many bits are in the entire address (e.g. /28).
This would give you a usable range of 10.1.0.1 - 10.1.0.15. The VCN’s CIDR block must not overlap with your on-premises network or another VCN you peer with.
Subnets - Required
A subnet in this instance is a carved-up set of IP addresses from the overarching CIDR Block of the VCN (as mentioned above).
For example:

A subnet can be specific to Availability Domains or used to segregate Instances and resources.
Route Tables - Required
Route tables are rules that route traffic from subnets to destinations outside the VCN by way of gateways or specially configured instances.
For example:

Internet Gateways - Optional
An internet gateway allows your instances to access the internet. Once you have created the gateway you must add a rule in the route table to allow your instance to access the internet gateway target.
Dynamic Routing Gateways Attachments
This allows traffic between your VCN and on-premises network. You can use an IPSec Tunnel or FastConnect. Be sure to create the DRG before setting up the Attachment.
Network Security Groups - Optional
NSGs operate in a different way than security lists. NSGs let you separate your VCN's subnet architecture. They consist of a set of ingress and egress rules that apply only to a set of VNICs of your choice in a single VCN.
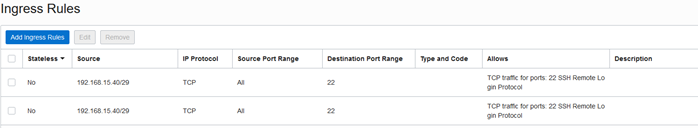
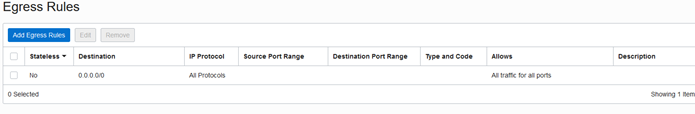
Security Lists - Required
Security rules are virtual firewall rules for your VCN. OCI creates a default security list. This needs editing to match your security rules.
Ingress - Inbound rules
Egress - Outbound rules
DHCP Options – Optional
DHCP options allow the instance to pick up DHCP assigned networking on boot up.
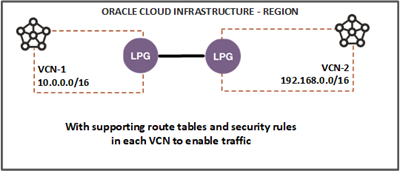
Local Peering Gateways - Optional
This allows a VCN to route traffic to another peered VCN.
Source: https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Network/Tasks/localVCNpeering.htm
NAT Gateways – Optional
Allows resource without public IP access to the internet without allowing any incoming traffic. Useful for Patching and updating.
Service Gateways - Optional
Allows recourses within your VCN to include other examples.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Terminology
As with all cloud-based vendors, terminology changes.
This document posted by Oracle, explains key terminology you will need to know before creating your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Our previous blog also explains more about instance and database acronyms to further your understanding of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure before you start.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Network Architecture
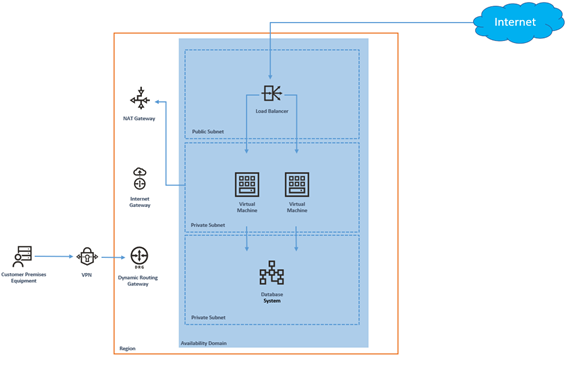
Let’s see how a simple OCI network architecture appears as a design.
This diagram shows a basic Oracle cloud deployment. This includes an Availability Domain/compartment with a VCN attached with three separate subnets. Note that a NAT gateway and Internet gateway are also set up for the VCN.
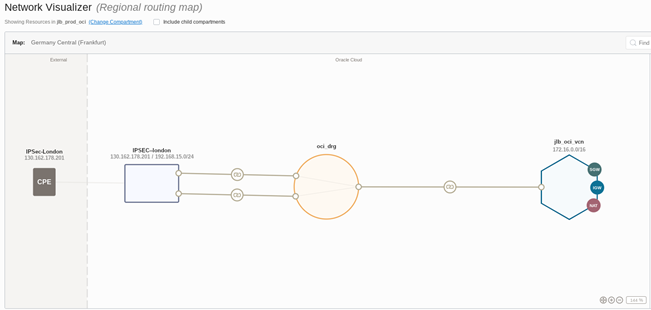
OCI Network Visualizer of the Above Diagram
Once you have created the VCN and all the resources needed there is a Network Visualizer page this will automatically map the current layout of your VCN. Here you can see how the VCN is connected to the on-premises Endpoint over IPSec. You will also note two tunnels are created from the DRG to the IPsec profile.
Conclusion
You can set up a simple VCN and follow the below steps to create the resources you need:
- Create a tenancy
- Create a Compartment
- Create a VCN attached to the newly created Compartment
- Create each Resource needed for your deployment
You can also simplify these steps by using the Oracle Cloud Virtual Networking QuickStart Wizard. Here you will be able to create and configure each resource needed.
Remember to familiarise yourself with each resource type and feature before setting up an Oracle Cloud deployment and it's always useful to plan ahead and gather any information you may need prior to starting a cloud deployment.
If you are interested in our specialist Oracle Cloud Services, please contact one of our expert Oracle Cloud Consultants. You can also email us at enquiries@dsp.co.uk or book a meeting.

.png?width=250&name=stonewater-logo%20(1).png)